AMD has officially unveiled its highly anticipated Ryzen 9000 “Zen 5” Desktop CPUs, boasting up to 16 cores and substantial IPC (Instructions Per Cycle) gains compared to the previous Zen 4 architecture. This new lineup, codenamed Granite Ridge, aims to set new standards in high-performance computing, particularly for gaming PCs.
Introduction to Zen 5 Architecture
The Ryzen 9000 series is built on AMD’s latest Zen 5 core architecture, featuring significant enhancements over its predecessor. Key improvements include:
- Improved Branch Prediction: Enhanced accuracy and reduced latency in branch prediction.
- Higher Throughput: Wider pipelines and vectors for increased data processing capabilities.
- Increased Parallelism: Deeper window size across the design for more simultaneous operations.
Zen 5 introduces up to a 2x increase in several critical performance areas, such as instruction bandwidth for front-end instructions, data bandwidth between L2 and L1 caches, and AI performance via AI and AVX512 throughput. The CPU cores (CCDs) are fabricated on TSMC’s 4nm process node, while the I/O die (IOD) uses the 6nm process node. This architecture retains the peak configuration of two CCDs and one IOD on consumer platforms.
IPC Uplift and Cache Enhancements
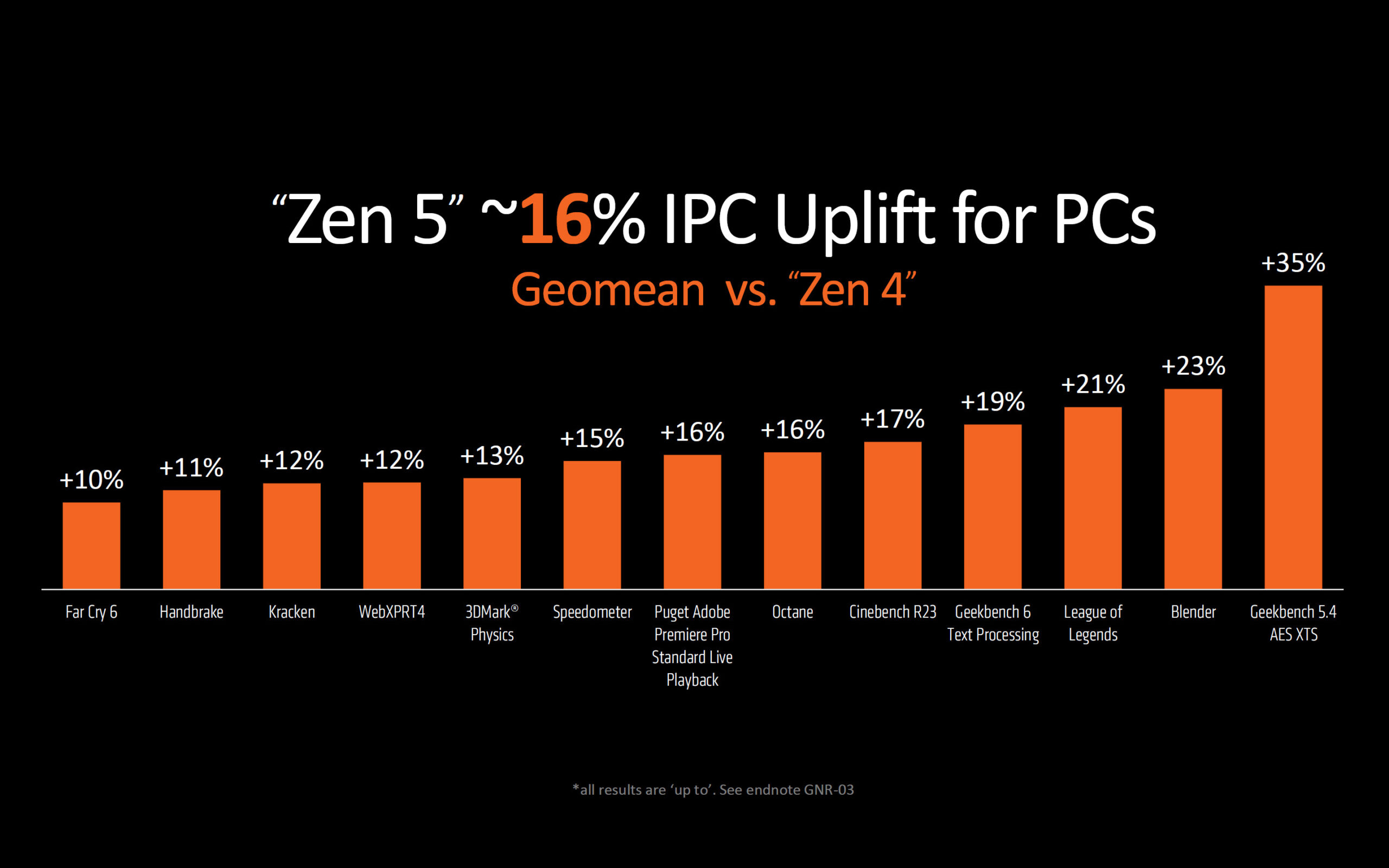
The Zen 5 architecture comes with an impressive IPC uplift, averaging a 16% increase over Zen 4. In some specific scenarios, such as Geekbench 5.4’s AES XTS test, the IPC gain can reach up to 35%. The cache system has also been revamped, with significant improvements in L2 and L3 cache structuring. The integrated memory controller (IMC) has been optimized to support higher EXPO/XMP memory speeds, with the Infinity Fabric clock boosted from 2000 MHz (Zen 4) to 2400 MHz (Zen 5), and native DDR5-5600 support.
Ryzen 9000 Desktop CPU Lineup
The initial lineup of the Ryzen 9000 “Granite Ridge” family includes four SKUs:
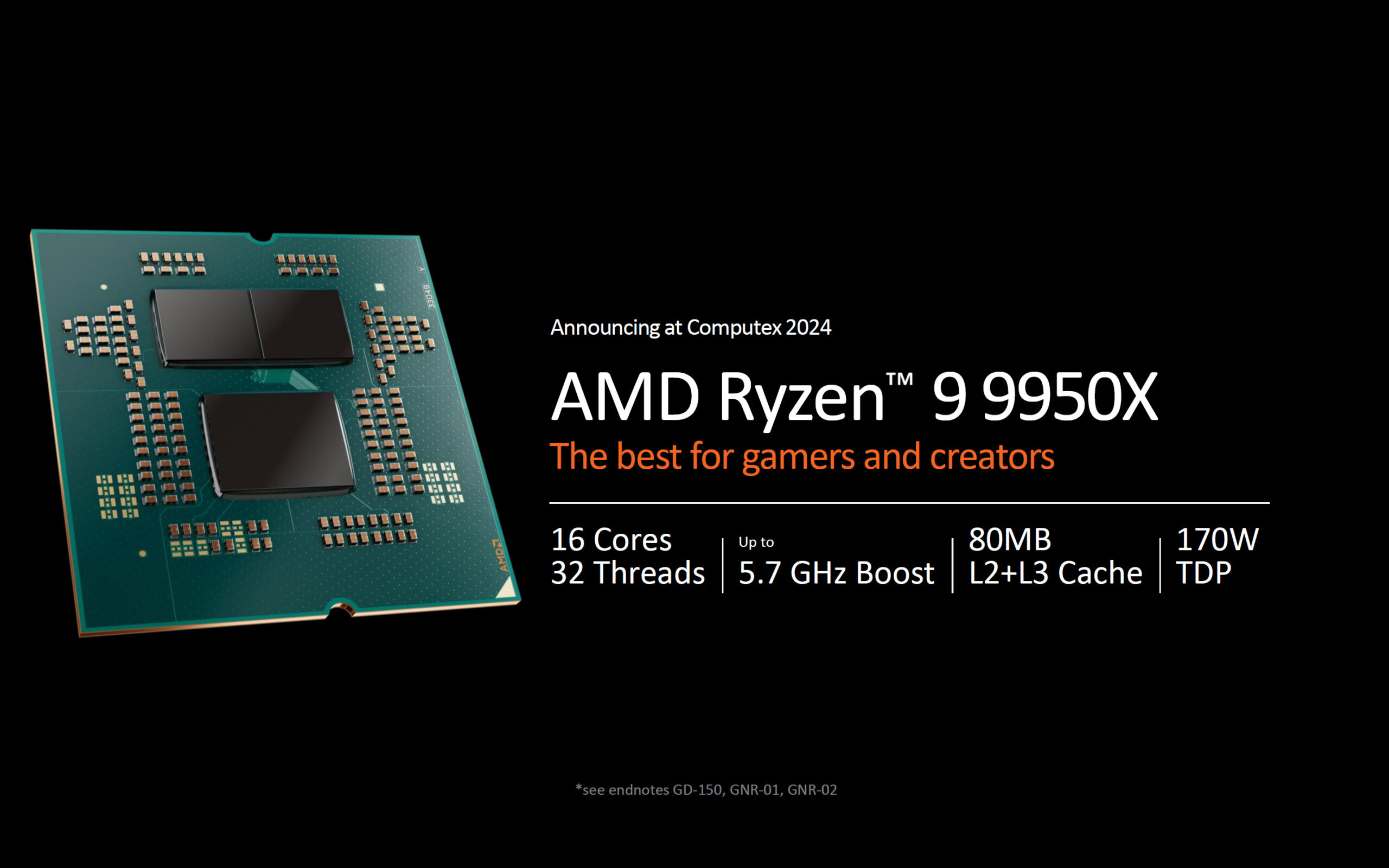
- Ryzen 9 9950X: The flagship model features 16 cores and 32 threads, with a maximum boost clock of 5.7 GHz. It includes 80 MB of cache (64 MB L3 + 16 MB L2) and maintains a TDP of 170W, similar to the Ryzen 9 7950X.
- Ryzen 9 9900X: This 12-core, 24-thread CPU has a boost clock of up to 5.6 GHz and a 76 MB cache. It stands out with a reduced TDP of 120W, down from the 170W of the Ryzen 9 7900X.
- Ryzen 7 9700X: Targeted at mainstream users, this 8-core, 16-thread processor offers a boost clock of 5.5 GHz, 40 MB of cache (32 MB L3 + 8 MB L2), and a notably lower TDP of 65W compared to the 105W of the Ryzen 7 7700X.
- Ryzen 5 9600X: This 6-core, 12-thread CPU features a maximum boost clock of 5.4 GHz, 38 MB of cache, and a 65W TDP, mirroring the reduction seen in the Ryzen 7 9700X.
Performance Insights
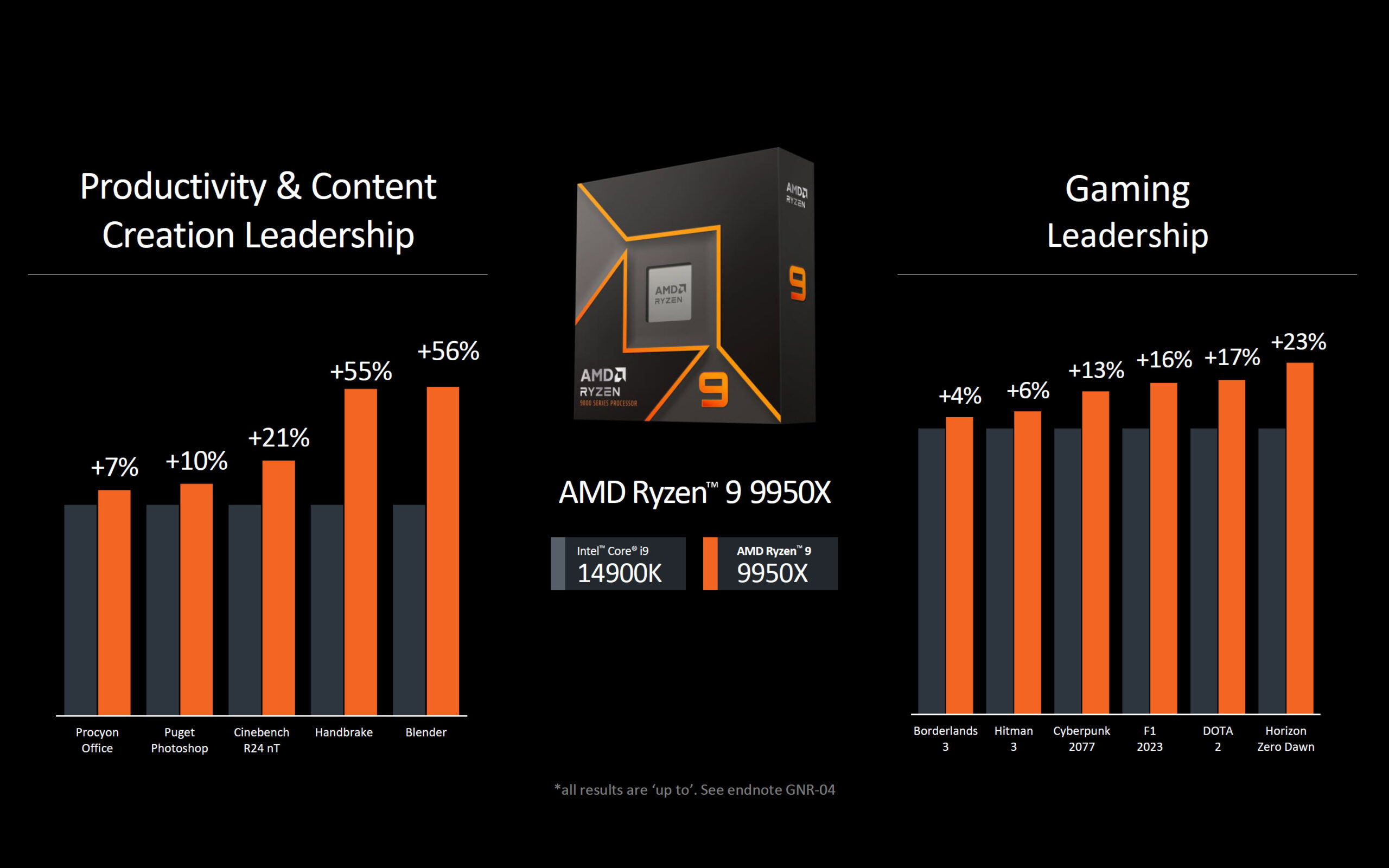
AMD has provided performance comparisons for its Ryzen 9000 series, specifically pitting the Ryzen 9 9950X against Intel’s Core i9-14900K. The Ryzen 9 9950X shows a remarkable 56% improvement in productivity tasks (with an average uplift of 29.8%) and a 23% increase in gaming performance (with an average uplift of 13.2%). This positions it well ahead of Intel’s flagship in both domains.
In gaming, the Ryzen 9 9950X is expected to outperform the previous Zen 4 3D V-Cache chips, with the upcoming Zen 5 3D V-Cache models likely extending this lead further. The gaming performance boost is attributed to reduced latencies in the new architecture.
For content creators and AI applications, the Ryzen 9000 series promises a 100% increase in graphics bandwidth, thanks to dedicated PCIe 5.0 lanes, and a 20% AI acceleration in large language models (LLMs) such as Mistral. While AMD has not integrated a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) in these CPUs, the architectural improvements alone deliver superior AI performance compared to the competition.
Pricing and Availability
While AMD has yet to disclose specific pricing details for the Ryzen 9000 series! the new CPUs are expected to be priced similarly to the Ryzen 7000 series. The Ryzen 9000 CPUs are set to launch in July this year! with further updates anticipated as the release date approaches.
Conclusion
With the introduction of the Ryzen 9000 “Zen 5” Desktop CPUs, AMD continues to push the boundaries of high-performance computing. The substantial IPC gains, architectural enhancements, and competitive performance metrics against Intel’s latest offerings underscore AMD’s commitment to delivering cutting-edge technology to gamers and content creators alike. As the release date draws nearer, anticipation builds for the impact these new processors will have on the market.